Ectopia Lentis In Marfan Syndrome
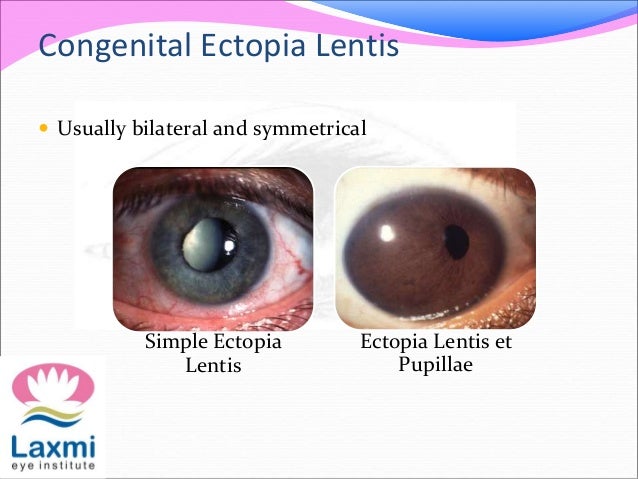
Ectopia lentis in marfan syndrome. Ectopia lentis AND a FBN1 mutation associated with Aortic Root Dilatation Marfan syndrome - In the presence of ectopia lentis but absence of aortic root dilatationdissection the identification of an FBN1 mutation previously associated with aortic disease is required before making the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome. Disease or Syndrome The spectrum of ADAMTSL4-related eye disorders is a continuum that includes the phenotypes known as autosomal recessive isolated ectopia lentis and ectopia lentis et pupillae as well as more minor eye anomalies with no displacement of the pupil and very mild displacement of the lens. Epub 2015 Aug 18.
Developmental ectopia lentis subluxation of the lens occurs in 50 to 80 of persons with the autosomal dominant hereditary disease Marfan syndrome. Approximately 60 of MFS patients with FBN1 gene mutation will suffer ectopia lentis EL from the. Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disease resulting from various mutations to the fibrillin-1 gene located on chromosome 15.
The Marfan syndrome had been diagnosed clinically in 28 families ectopia lentis in 2 congenital contractural arachnodactyly in 3 mitral-valve prolapse syndrome in. A 27-year-old woman with Marfans syndrome presented with worsening vision and glare in each eye. This may be present at birth.
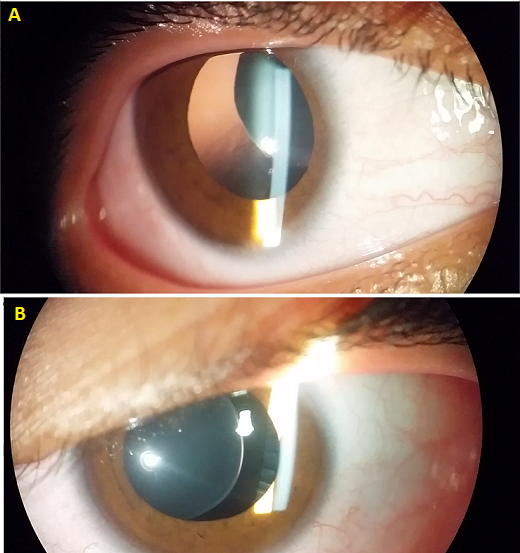
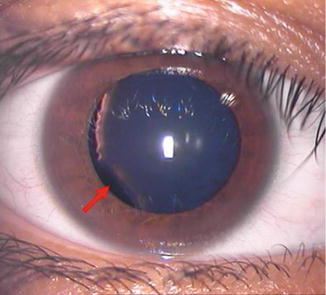
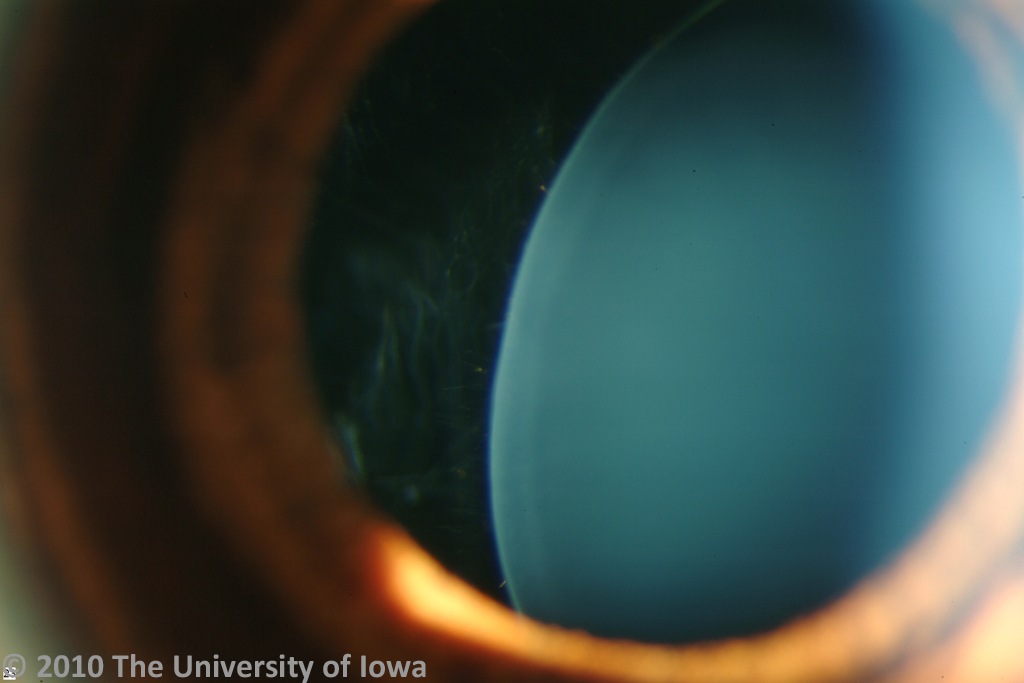
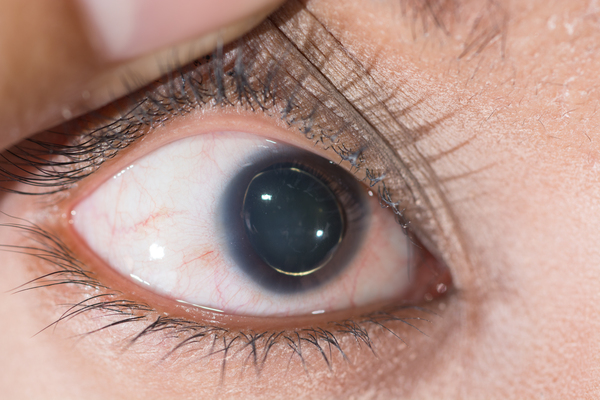
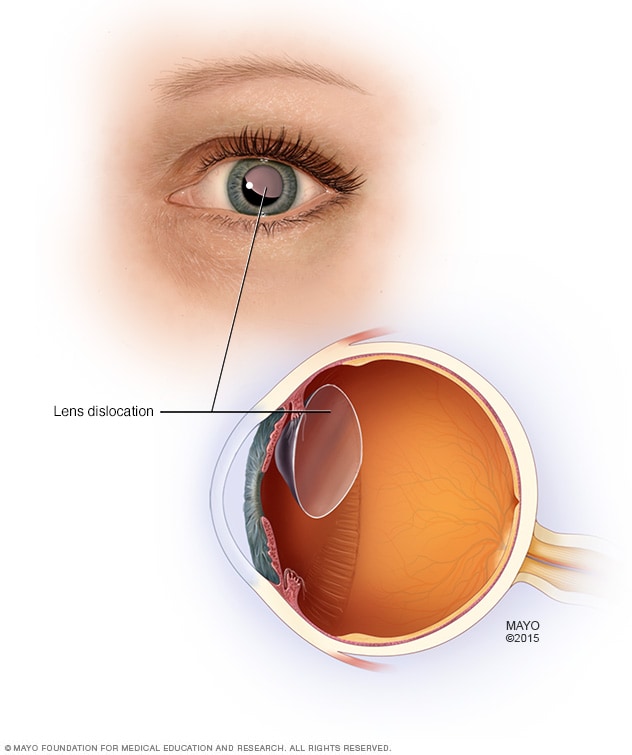
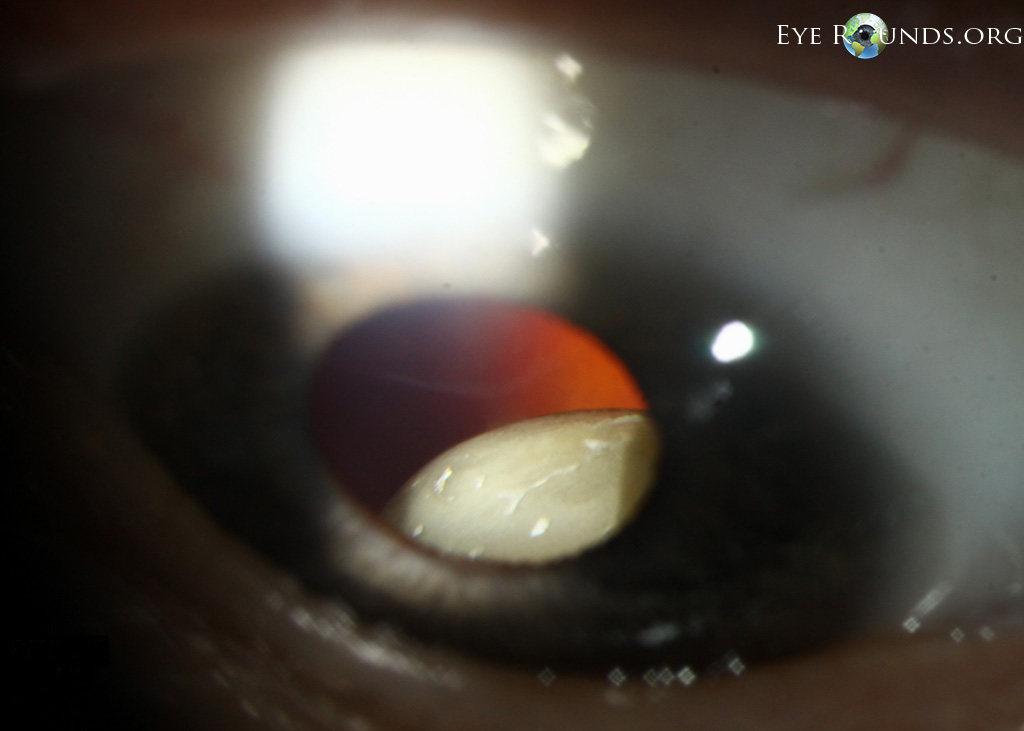
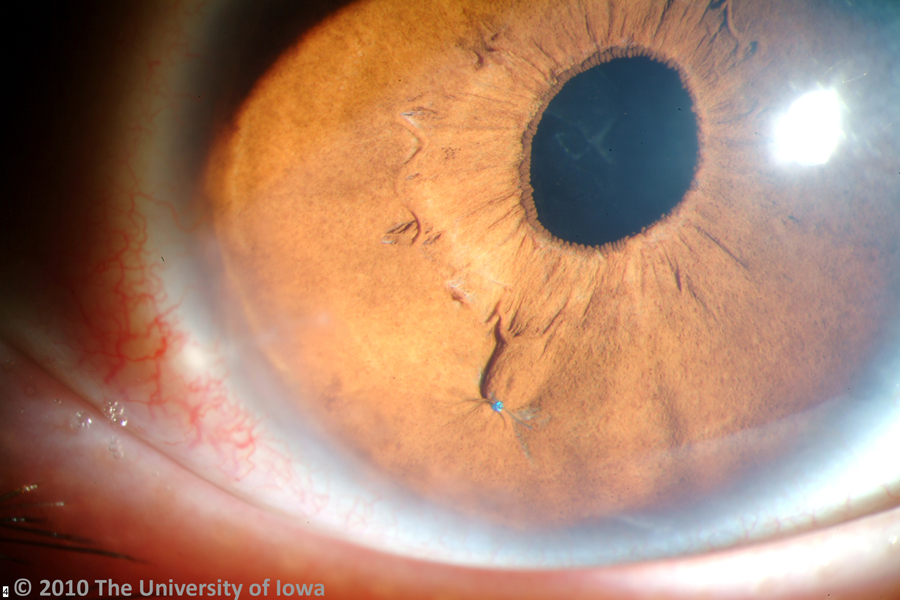
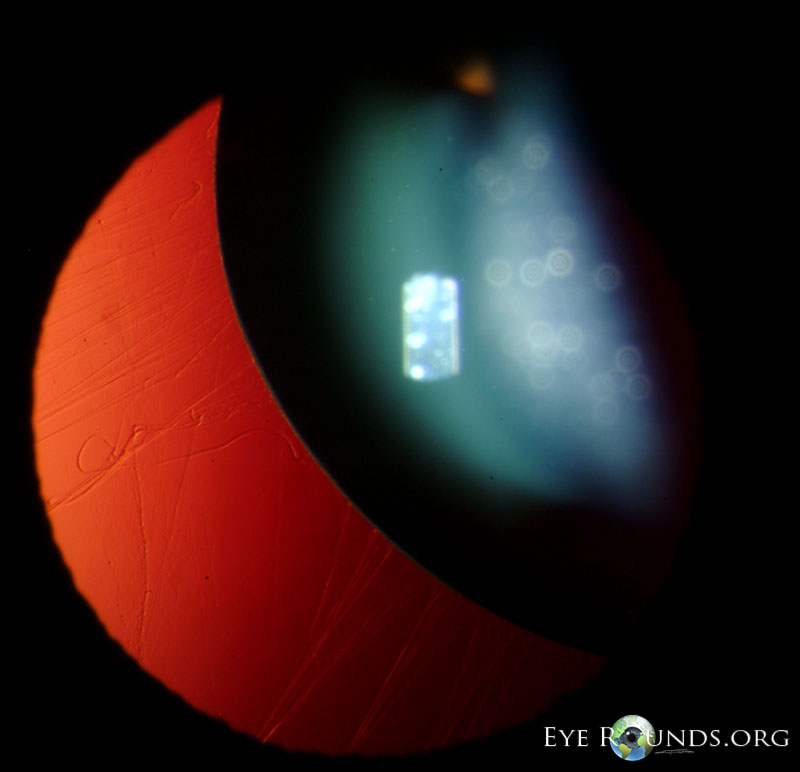
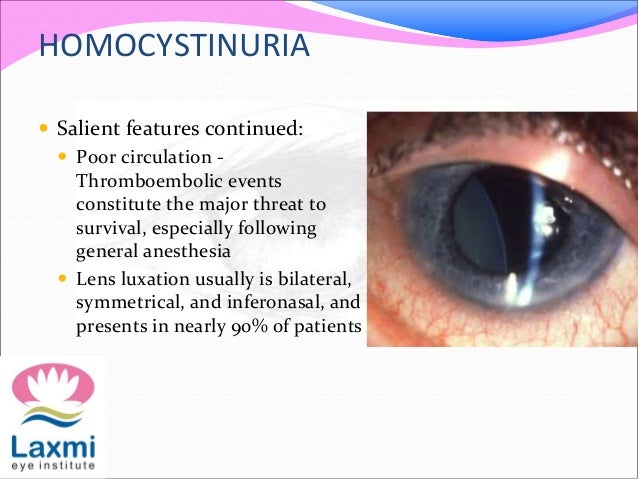
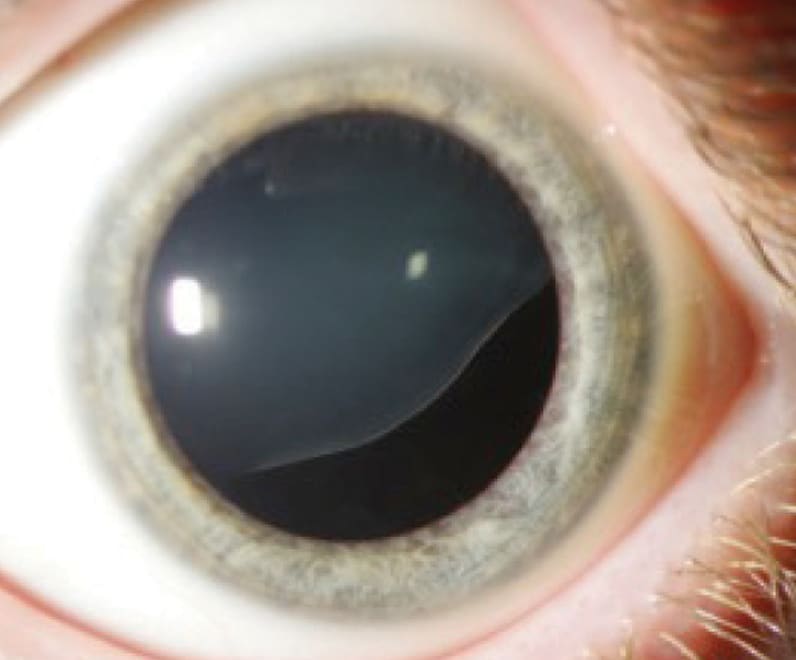
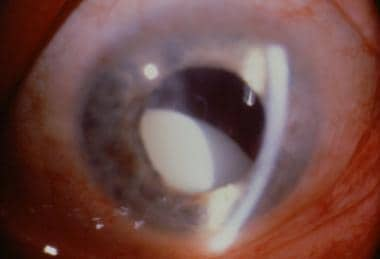
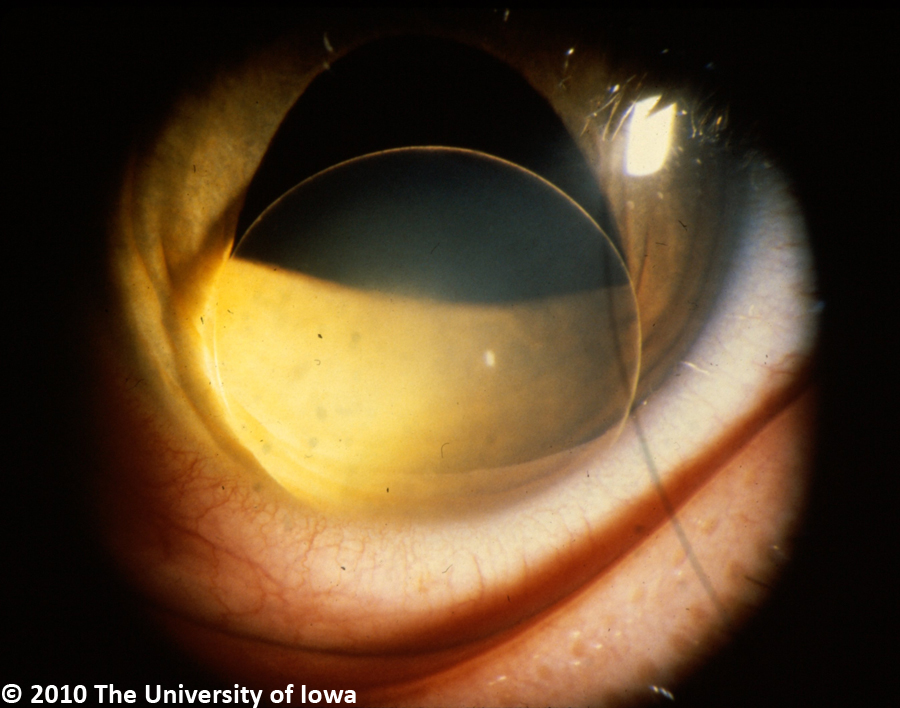
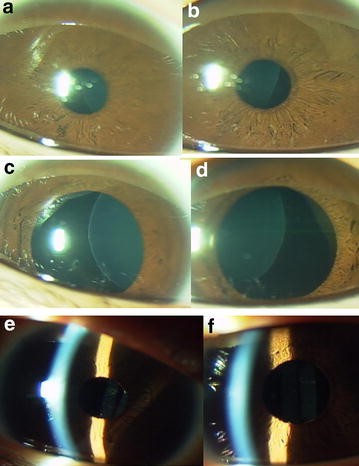
The lens dislocation is usually supratemporal Figures and is almost always bilateral and fairly symmetrical. Ectopia Lentis in Marfans Syndrome David R. Ectopia lentis is the most common ocular manifestation in MFS with FBN1 mutation as described in the seminal paper by Maumenee in 1981 3 and is relatively specific to this disease when associated with other features.
This combination of features is called ectopia lentis syndrome. Marfan syndrome MFS is a multisystem connective tissue disorder with primary involvement of the ocular cardiovascular and skeletal systems. To determine the effectiveness of combined pars plana vitrectomy-lensectomy and open-loop anterior chamber lens implantation for the management of ectopia lentis associated with Marfan syndrome.
The major ocular finding of Marfan syndrome MFS is ectopia lentis and approximately 60 of patients have lens dislocation which is usually superior and temporal. Marfan syndrome Marfan syndrome is the most common cause of heritable ectopia lentis and ectopia lentis is the most frequent ocular manifestation of Marfan syndrome occurring in approximately 75 of patients. Marfan syndrome MFS is a hereditary disease with an incidence of 03 in the general population.
Common ocular abnormality of Marfans syndrome is ectopia lentis occurring in 50 to 80 of affected individuals 13. ECTOPIA LENTIS SYNDROME In some families dislocation of the lens of the eye ectopia lentis is the predominant feature that passes from generation to generation.
Disease or Syndrome The spectrum of ADAMTSL4-related eye disorders is a continuum that includes the phenotypes known as autosomal recessive isolated ectopia lentis and ectopia lentis et pupillae as well as more minor eye anomalies with no displacement of the pupil and very mild displacement of the lens.
The Marfan syndrome had been diagnosed clinically in 28 families ectopia lentis in 2 congenital contractural arachnodactyly in 3 mitral-valve prolapse syndrome in. Lally MD and Julia Monsonego CRA. Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disease resulting from various mutations to the fibrillin-1 gene located on chromosome 15. Marfan syndrome MFS is a hereditary disease with an incidence of 03 in the general population. Developmental ectopia lentis subluxation of the lens occurs in 50 to 80 of persons with the autosomal dominant hereditary disease Marfan syndrome. Sometimes this occurs along with some of the skeletal bone and joint features of Marfan syndrome. The major ocular finding of Marfan syndrome MFS is ectopia lentis and approximately 60 of patients have lens dislocation which is usually superior and temporal. Ectopia lentis AND a FBN1 mutation associated with Aortic Root Dilatation Marfan syndrome - In the presence of ectopia lentis but absence of aortic root dilatationdissection the identification of an FBN1 mutation previously associated with aortic disease is required before making the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome. Disease or Syndrome The spectrum of ADAMTSL4-related eye disorders is a continuum that includes the phenotypes known as autosomal recessive isolated ectopia lentis and ectopia lentis et pupillae as well as more minor eye anomalies with no displacement of the pupil and very mild displacement of the lens.
Disease or Syndrome The spectrum of ADAMTSL4-related eye disorders is a continuum that includes the phenotypes known as autosomal recessive isolated ectopia lentis and ectopia lentis et pupillae as well as more minor eye anomalies with no displacement of the pupil and very mild displacement of the lens. Ectopia lentis AND a FBN1 mutation associated with Aortic Root Dilatation Marfan syndrome - In the presence of ectopia lentis but absence of aortic root dilatationdissection the identification of an FBN1 mutation previously associated with aortic disease is required before making the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome. The lens dislocation is usually supratemporal Figures and is almost always bilateral and fairly symmetrical. Retrospective review of the medical records of 4 consecutive patients with Marfan syndrome who underwent combined pars plana lensectomy-vitrectomy. Marfan syndrome MFS is a hereditary disease with an incidence of 03 in the general population. A 27-year-old woman with Marfans syndrome presented with worsening vision and glare in each eye. Sometimes this occurs along with some of the skeletal bone and joint features of Marfan syndrome.




























Post a Comment for "Ectopia Lentis In Marfan Syndrome"