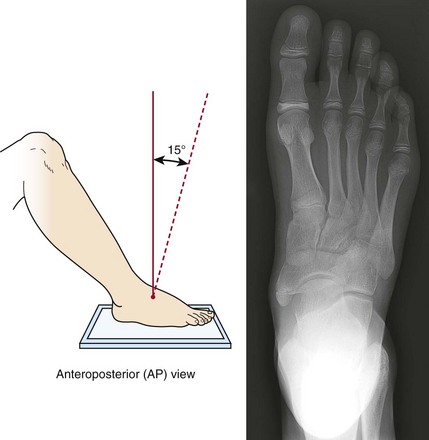
Foot Ct Scan Position
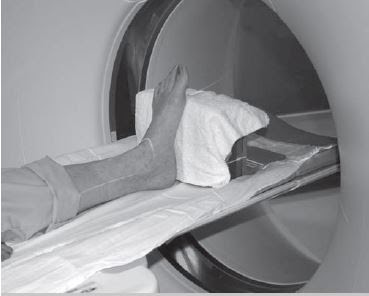
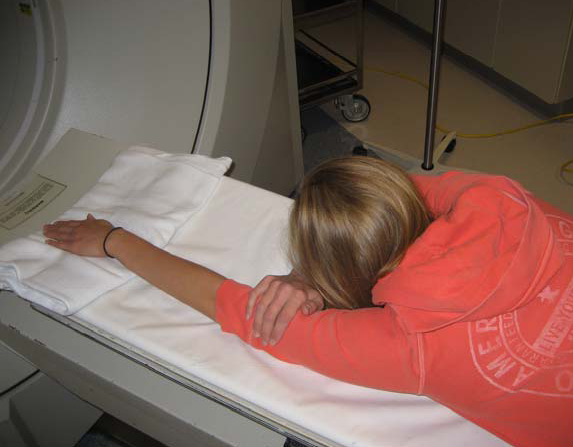
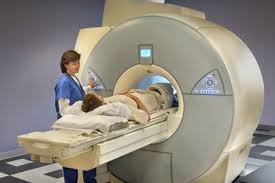
Foot ct scan position. Imaging is performed with the patient in prone. The foot is typically held in a neutral position and sagittal and axial images are taken of the tendon. And even the positioning of your foot and the relief you get when you hold your foot in a different position can tells a lot about whether or not an MRI or CT scan will be helpful for you.
SPECT high resolution CT images left to right. Color sonography can also been used to detect posterior tibial tendinopathy. Although there are methods to simulate the standing position while the patient is lying on a table the best way to evaluate foot and ankle biomechanics is to have the patient stand.
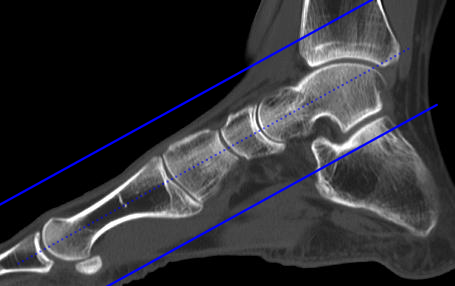
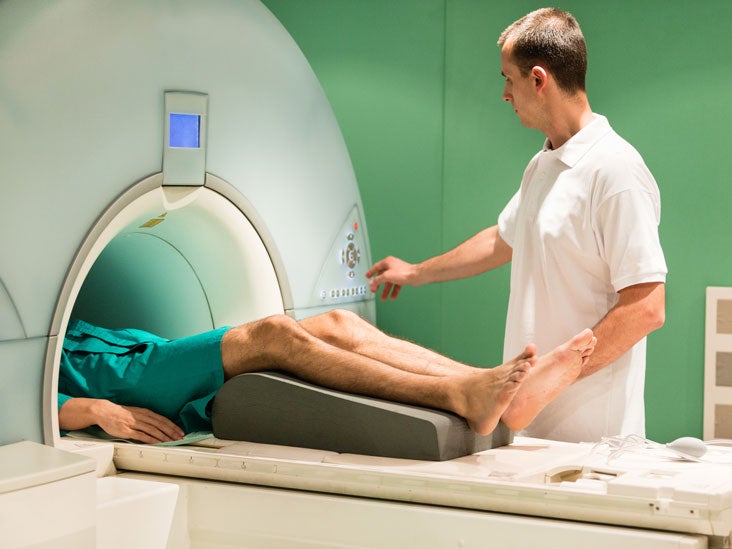
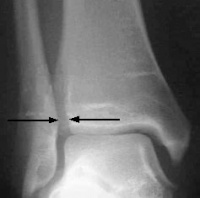
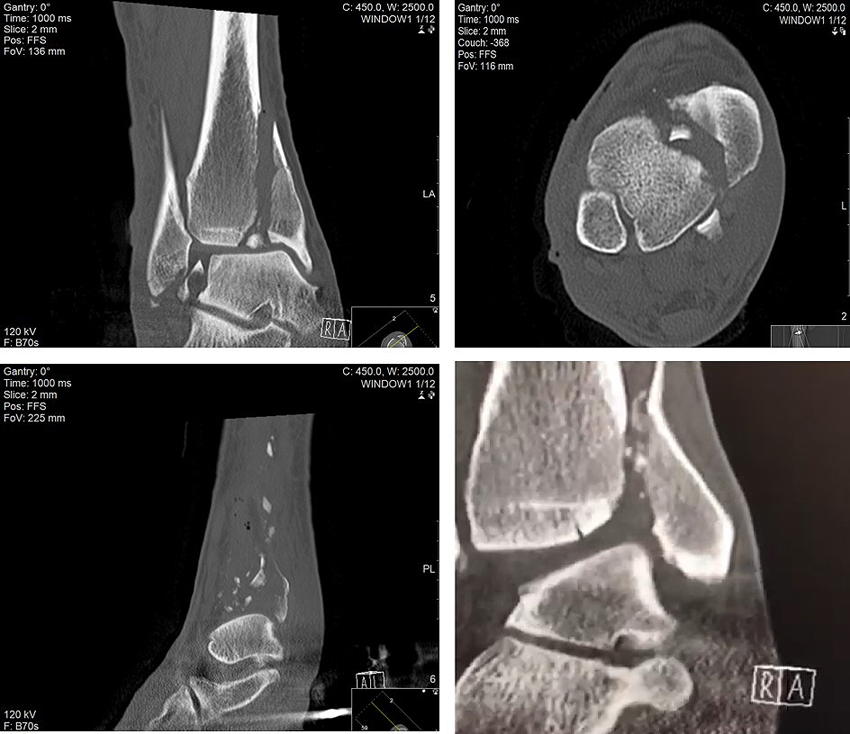
Transverse sagittal and coronal of the left foot of a 21-year-old female with an os tibiale externum in both feet and a history of fixation of the os tibiale externum at the left side with persistent painSPECT-CT shows high focal activity in the os tibiale externum at the left side indicative of nonunion. Relevant Anatomy C a l c a n e u s C u b o i d L a t e r a l C u n e i f o r m M e d i a l C u n e i f o r m I n t r m e d i a t e u n e f o r m. Patient Supine with feet first into scanner Keep knees extended side- by-side.
They also show soft tissues such as cartilage ligaments and muscles more clearly than traditional X-rays so they are more useful for diagnosing. The foot is prone to several types of damage and injuries. Make mortise coronal and sagittal MPRs as depicted below using thin data set with sharp kernel.
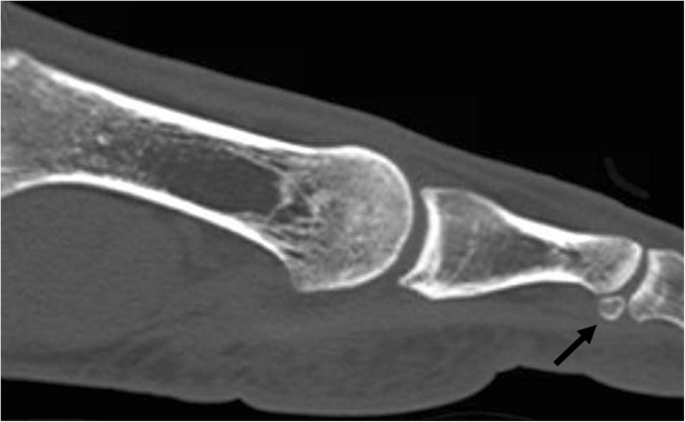
CT scans help doctors distinguish between a simple cyst and a solid tumor and any involvement of the bone. In a traditional CT scan the foot is in a relaxed position. Above tibiafibula joint through hind foot.
Foot and Ankle CT Scan CT scans may be used to diagnose ankle fractures that dont show up on X-ray. Pain and inflammation of the foot may cause limited movement 5. Although there are methods to simulate the standing position while the patient is lying on a table the best way to evaluate foot and ankle biomechanics is to have the patient stand.
In a traditional CT scan the foot is in a relaxed position. Positioning Patient supine.
Medical professionals use advanced imaging procedures to diagnose medical problems in the foo t.
Color sonography can also been used to detect posterior tibial tendinopathy. Positioning Patient supine. In a traditional CT scan the foot is in a relaxed position. Microsoft PowerPoint - MSK CT PROTOCOL2 Author. A computed tomography scan of the foot and ankle may help doctors examine any injury or fractures 6. Although there are methods to simulate the standing position while the patient is lying on a table the best way to evaluate foot and ankle biomechanics is to have the patient stand. The foot is typically held in a neutral position and sagittal and axial images are taken of the tendon. And even the positioning of your foot and the relief you get when you hold your foot in a different position can tells a lot about whether or not an MRI or CT scan will be helpful for you. A CT scan of the foot allows physicians to examine bones soft tissues and joints to determine whether there are any damages fractures or any further abnormalities.
7212015 100450 AM. Scan through entire foot. The foot is typically held in a neutral position and sagittal and axial images are taken of the tendon. Imaging is performed with the patient in prone. And even the positioning of your foot and the relief you get when you hold your foot in a different position can tells a lot about whether or not an MRI or CT scan will be helpful for you. Computed tomography offers some advantages over other x-ray techniques in diagnosing disease particularly because it clearly shows the shape and exact location of soft tissues and bones in any slice of the foot and ankle. Although there are methods to simulate the standing position while the patient is lying on a table the best way to evaluate foot and ankle biomechanics is to have the patient stand.















/doctor-preparing-patient-for-mri-103919304-5a36bf2c0d327a00379fb318.jpg)












Post a Comment for "Foot Ct Scan Position"